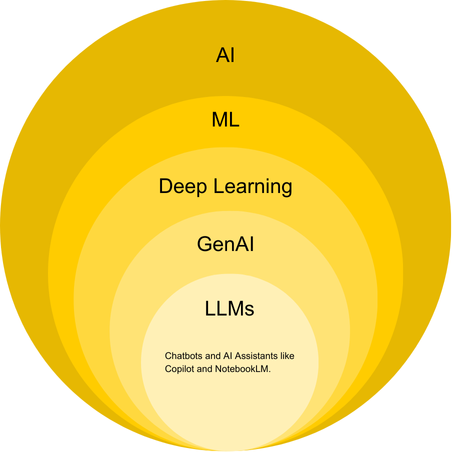
AI learns, predicts and generates content.
- AI learns by studying examples (data) to recognize patterns, much like how people learn by exploring concepts, practicing and observing the world around them.
- AI predicts by using what it’s learned to answer questions, provide suggestions or even create new content.
- AI generates new content (text, images, code, etc.).
Simply put, AI doesn’t "think" like humans—it learns from data, predicts what makes sense based on its training and generates new content by identifying patterns in vast amounts of information.